Day Trading and Swing Trading
This course delves into the core principles and execution strategies of day trading and swing trading, helping learners understand the risk characteristics and profit logic of different time frames, and establish their own active trading system.
Understanding Active Trading Strategies
In the cryptocurrency market, investors can be broadly divided into two categories:
- Active Traders, who profit from short-term market fluctuations;
- Passive Investors, who tend to hold for the long term and capture trend-based returns.
This course will focus on the two most common strategies among active traders: Day Trading and Swing Trading. Both rely on market volatility but differ significantly in time frames, analysis methods, and risk management.
Day Trading
1. Core Definition
Day trading refers to completing buy and sell operations within the same trading day, with traders not holding positions overnight. This strategy emphasizes capturing short-term price movements and relies on high-frequency decision-making and strict discipline.
2. Strategy Logic
The core of day trading is “capturing small fluctuations and accumulating small gains.” Traders typically use technical indicators (such as RSI, MACD, Bollinger Bands) or price patterns to determine entry and exit points. For example, when BTC price breaks through key support or resistance levels, traders might complete multiple operations within minutes or hours.
3. Advantages and Challenges
Advantages:
- Short market risk exposure time, effectively avoiding overnight volatility;
- Clear profit and loss, daily settlement results.
Challenges:
- Highly dependent on attention and execution;
- Higher transaction fees and slippage costs;
- High emotional management pressure, easy to over-trade.
4. Suitable for
Suitable for traders who are sensitive to market fluctuations, can make quick decisions, and are willing to invest a lot of time. For beginners, without experience or discipline, it’s easy to amplify losses due to frequent operations.
Swing Trading
1. Core Definition
Swing trading typically involves holding positions for several days to weeks, with traders aiming to profit from medium-term trend fluctuations. Unlike day trading, swing trading focuses more on trend structure and market rhythm rather than short-term fluctuations.
2. Strategy Logic
The goal of swing trading is to capitalize on “a segment of movement within a trend,” also known as “a swing.” Common tools include trendlines, moving averages, and Fibonacci retracements to identify support and resistance zones.
Example: If ETH pulls back to support after breaking a significant resistance level, a swing trader might choose to enter a position during the retracement and hold for several days waiting for the next upward move.
3. Advantages and Challenges
Advantages:
- Lower trading frequency, reducing transaction fee burden;
- More flexible time requirements, can be combined with other work schedules;
- Easier to develop systematic strategies in conjunction with technical analysis.
Challenges:
- Overnight risk exists, prices may be affected by sudden news;
- Requires stronger patience and medium-term judgment ability.
4. Suitable for
Swing trading is more suitable for investors with certain analytical skills who want to balance risk and time investment. It strikes a relative balance between “short-term flexibility” and “long-term trend following.”
Core Differences Between Day and Swing Trading
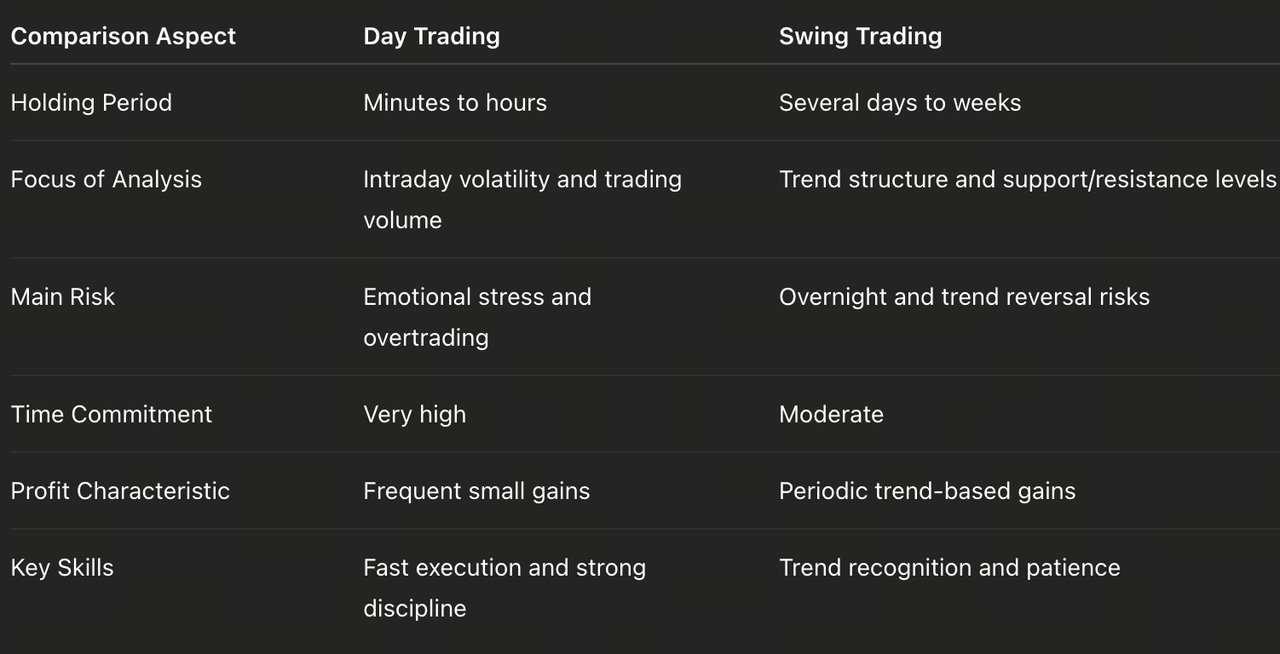
Risk Management and Execution Discipline
Regardless of the strategy adopted, risk management is the core condition for success. For both day and swing traders, common disciplines include:
- Stop-loss Setting: A stop-loss price should be determined before entering each trade and must be executed once triggered.
- Position Management: A single position should not exceed 5% of the total account funds to prevent amplification of single losses.
- Backtesting and Recording: Record the reasons, mindset, and results of each trade, summarizing effective patterns from historical data.
- Emotional Control: Market volatility can easily induce anxiety and greed. Calm and regular routines are prerequisites for long-term stability.
Case Study: Comparison of BTC Day and Swing Trading Operations
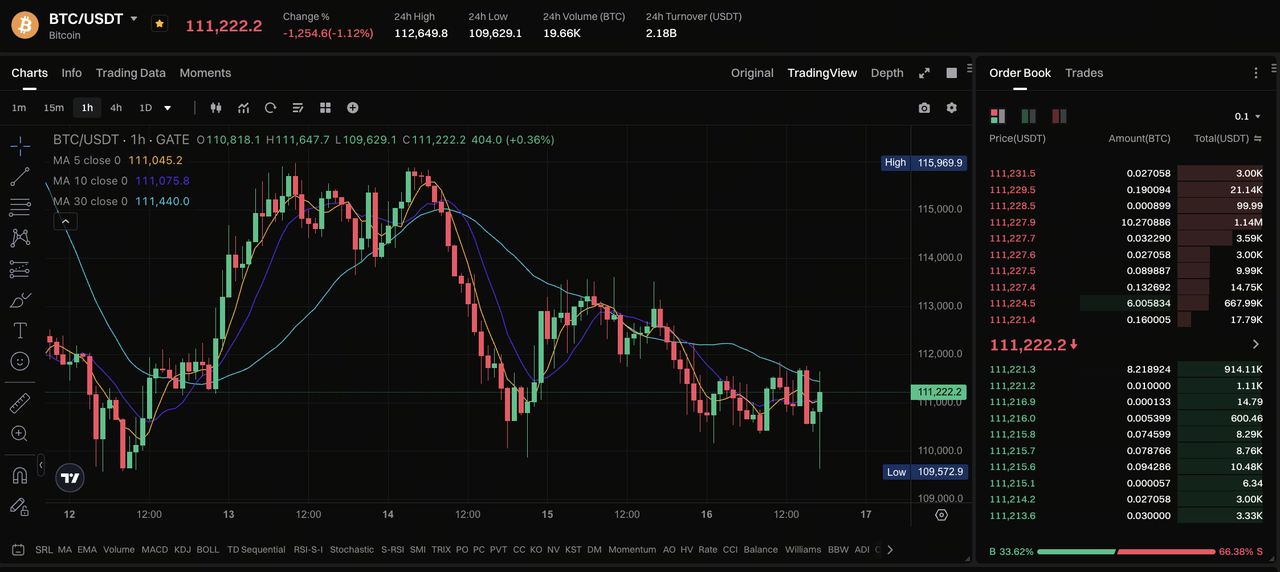
Source: https://www.gate.com/trade/BTC\_USDT
Taking the BTC/USDT 1-hour chart on October 16, 2025, as an example, the current price is around 111,222 USDT, with a 24-hour range between 109,629–112,649, overall in a fluctuating downward phase.
Day Trading Perspective
Trading Logic: Mainly focused on capturing short-term fluctuations, paying attention to moving average crossovers and 1h structure changes.
Current Signal: MA5 and MA10 are still below MA30, short-term bears dominate, but signs of bottom volume rebound appear.
Operation Strategy:
- Entry: Attempt to buy low around 111,000
- Stop-loss: Below 110,000
- Take-profit: 112,500 level
- Trading Period: Complete within hours
Key Focus: Quick reaction, take profits promptly, avoid overnight holding risks.
Swing Trading Perspective
Trading Logic: Follow the medium-term trend, hold positions for several days to observe structural breakouts.
Current Signal: If the price can break and stabilize above 112,800, it may form a short-term rebound swing.
Operation Strategy:
- Entry: Enter after confirmation of 112,800 breakout and pullback
- Stop-loss: Below 110,500
- Target: 115,000–116,000 range
- Trading Period: 2–4 days
Key Focus: Patiently wait for trend signal confirmation, emphasizing “swing range over frequency.”
Conclusion
Day trading and swing trading are two mainstream active strategies in the crypto market. Their differences lie not only in time frames but also in mindset:
- Day trading pursues immediate decision-making and speed;
- Swing trading emphasizes patience and trend judgment.
For beginners, it’s recommended to start with swing trading, establish a stable analytical framework and risk control awareness, then gradually transition to higher-frequency operations. Opportunities always exist in the market, but a stable system and self-discipline are the core to long-term success. In the current BTC structure, day trading is suitable for capturing rebound rhythms, while swing traders should wait for trend reversal signals. The core difference between the two lies in time frames and mindset management, not which is better, but the matching of strategy and rhythm.





