Portfolio and Risk Management
This course will introduce the basic concepts of portfolio and risk management, helping you understand how to balance returns and risks in the crypto market. By learning about asset allocation, position management, and stop-loss strategies, you will master key methods for building a robust investment system.
Introduction: Why You Shouldn’t “Bet It All” on Investing
Have you ever heard the saying—“Don’t put all your eggs in one basket”?
This is the core philosophy of Portfolio Management. In crypto markets or traditional finance, investing is never a gamble, but a game of probability and risk. Whether you’re buying Bitcoin, Ethereum, US stock ETFs, gold, or bonds, every asset has fluctuations and uncertainties. If you invest all your funds in one target, your capital could shrink instantly when the market moves against you.
Portfolio management is about diversifying investments, optimizing allocations, and controlling risks to help you profit steadily in the long term, rather than having your account “wiped out” by a single violent fluctuation. Risk management is the key to helping you survive in market turbulence.
What is a Portfolio?
Simply put, a portfolio is an “investment basket” composed of multiple assets. Its core idea is that different assets don’t rise and fall in price simultaneously, and through proper combination, one can pursue more stable returns while controlling risk.
For example:
- Person A: Invests all money in Bitcoin, high-risk high-volatility portfolio, could halve in value with one crash
- Person B: 50% in Bitcoin, 30% in Ethereum, 20% in stablecoins, risk is diversified, when BTC falls ETH or stablecoins may offset some losses
- Person C: 40% in crypto assets, 40% in US stock index, 20% in gold, portfolio derives from low correlation between different markets, overall volatility is lower
The main difference between these three investment methods is the degree of “diversification”. The more diversified the portfolio, the less impact from single market risks.
Balancing Risk and Return
All investments involve a trade-off between risk and return. Generally, higher risk means higher potential returns; conversely, lower risk means lower returns.
You can think of investing like flying:
- Buying low-risk products like government bonds or stablecoin staking is like flying commercial—safe but slow;
- Buying altcoins or futures with leverage is like flying a fighter jet—fast and exciting, but one mistake could lead to a crash.
Excellent investors don’t pursue “fastest”, but “most stable”. They know how to control risks, allowing their portfolio to navigate through stormy waters.
How to Build Your Portfolio
For beginners, you can gradually build your portfolio following these five steps:
Step One: Determine Your Goals and Risk Tolerance
Before investing, ask yourself three questions:
- What is my investment goal? (e.g., wealth accumulation, passive income, long-term value preservation)
- How much asset volatility can I tolerate?
- What is my investment timeframe? (short-term/medium-term/long-term)
Investors with high risk tolerance can allocate more to volatile assets, while those with low risk tolerance are better suited for conservative stablecoin or bond-type allocations.
Step Two: Choose Suitable Asset Classes
Common asset types include:
- Cryptocurrencies (high risk, high return): BTC, ETH, mainstream public chain tokens
- Stablecoins (low risk): USDT, USDC, etc.
- Stocks or ETFs (medium risk): S&P500 index funds, etc.
- Gold / Precious metals (safe-haven assets)
- Cash / Savings (zero risk but no growth)
In the crypto market, your portfolio can include both on-chain assets and traditional market targets.
Step Three: Control Asset Proportions
A common mistake for beginners is: “I’m bullish on BTC, so I’ll put 100% of my funds into it.” This is actually very dangerous.
The correct approach is to allocate weights, for example:
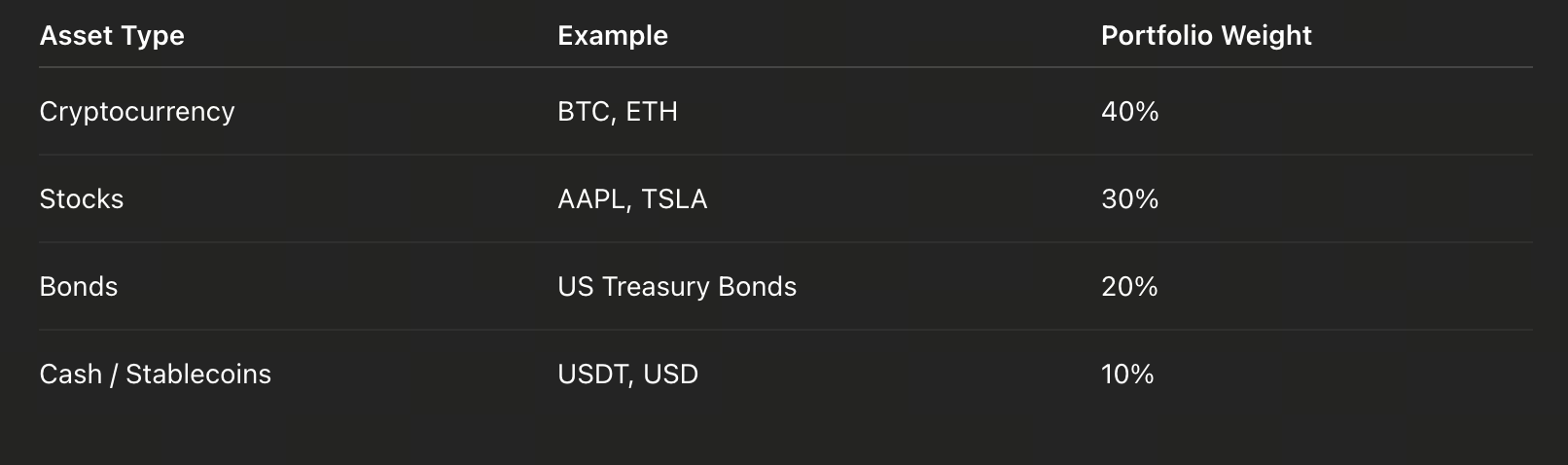
At the end of each quarter, you can check:
- If BTC rises too much causing its proportion to increase, you can sell some to return to the original weight;
- If ETH underperforms, you can buy more from the stablecoin portion;
- Meanwhile, dynamically adjust allocations based on market trends.
This way, your investment won’t become imbalanced due to a single asset’s surge or plunge.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Blindly going all-in: No cash reserve, forced to hold during market downturns.
- Frequent rebalancing: Frequent buying and selling in short term leads to fees and slippage losses.
- Lack of record-keeping: Not recording investment actions, don’t know where mistakes were made.
- Ignoring risk indicators: Only looking at returns, not volatility and drawdowns.
- Herd mentality: Following others when they profit, panic selling when losing.
Remember: Successful investing isn’t about luck, but about systems and discipline.
Establishing Your Own Investment System
An investment system isn’t a complex mathematical model, but a set of behavioral guidelines you can stick to long-term.
You can refer to this simple framework:
- Investment goals: Clear return targets and timeframes (e.g., 10% annual return, 3-year cycle)
- Asset allocation: Set proportions and write them in a table
- Risk control rules: Set stop-loss / take-profit / position limits
- Review frequency: Weekly or monthly review
- Keep a journal: Record each buy/sell, reasons, emotional state





